An Australian-first study has linked childhood eczema to natural fats found in babies’ skin.
Researchers hope this new discovery could identify children at risk of developing eczema in early screening programs.
University of Melbourne and Murdoch Research Children’s Institute researchers worked on the study with colleagues from the United States’ National Jewish Health.
They observed for the first time that babies’ skin lipids – a key structure in the skin – could predict which children would go on to develop eczema in Australian children.
It builds on a similar study conducted in South Korea in 2023.
“These are exciting findings,” senior author Professor Adrian Lowe said.
“This helps pave the way to prevent children from developing eczema.
“In the future, we may be able to use these lipids in screening programs to identify which babies are at risk of developing eczema.
“And also, these lipids may be used in skincare products to prevent eczema.”
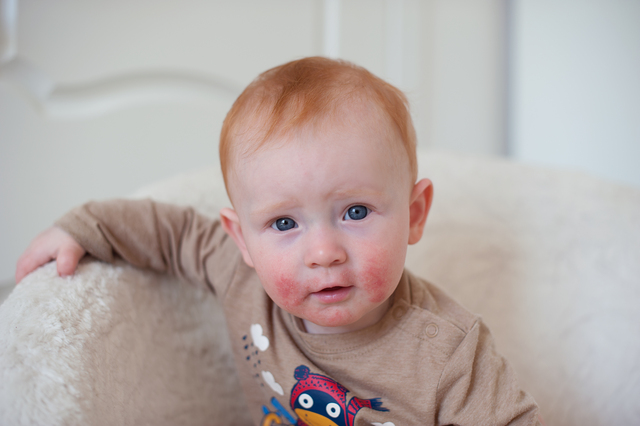
Eczema is the most common skin disease in children, with about one in three developing it in their first year of life.
The PEBBLES study included 133 infants in Australia.
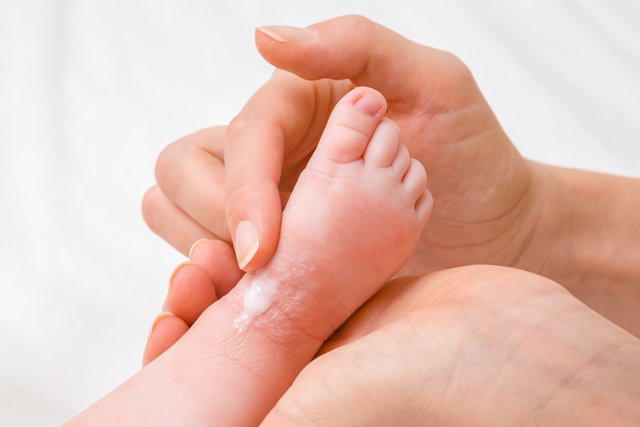
Skin lipids were collected from their forearms using a tape strip when they were six weeks old.
The researchers followed the children to see who developed eczema at age one and who did not.
Professor Lowe said those who did had a lower level of a particular type of lipid called protein-bound ceramides.
“This phenomenon has also been found in a study conducted in South Korea, highlighting that these lipids are important for the development of eczema,” he said.
“Currently, there are no effective ways to cure eczema despite advances in treatments in recent years.
“Several creams have been tested to prevent eczema, but they have not been effective.
“This may be because we were yet to determine which ingredients these creams need to contain.”
Professor Lowe said the next stage of research would involve testing creams that could promote the formation of protein-bound ceramides to see if they could prevent eczema.